Summary: In 2025, the global shift from degree-based hiring to skills-based talent management is reshaping workplaces. This blog explores how organizations can adopt skills-focused strategies to address talent shortages, boost innovation, and enhance inclusivity across diverse industries. It provides actionable steps, real-world examples, and 2025 trends like AI-driven skills mapping and micro-credentialing to ensure businesses stay competitive in a rapidly evolving economy.
The 2025 workplace demands agility, adaptability, and a focus on skills over traditional credentials. With automation, AI, and global competition reshaping industries, organizations must prioritize practical abilities to build resilient teams. A skills-based talent management strategy addresses talent shortages, fosters innovation, and promotes diversity, making it essential for industries like tech, finance, and healthcare. This blog explains what a skills-based strategy entails, its benefits, challenges, practical steps, and emerging trends to help organizations thrive globally.
Future-Ready HR with ZYNO HRMS
The modern workplace requires flexibility and a shift from credentials to skills. ZYNO HRMS empowers organizations with AI-driven insights, automated workflows, and analytics to identify, develop, and manage critical skills. By enabling skills-based hiring, personalized learning, and data-backed performance management, it helps close talent gaps and build resilient, diverse teams.
What Is a Skills-Based Talent Management Strategy?
A skills-based talent management strategy emphasizes employees’ abilities—such as coding, problem-solving, or leadership—over formal degrees. It involves:
- Hiring: Using practical assessments (e.g., coding exercises, case studies) to screen candidates, ensuring real-world problem-solving ability over academic credentials. AI-powered tools align candidate skills to job specifications for precise matches.
- Training: Offering targeted upskilling through bootcamps or micro-credentials. These short, flexible programs focus on evolving technologies or business needs, minimizing time to productivity.
- Career Development: Designing career paths based on skill mastery, enabling employees to advance through high-impact skills rather than fixed job ladders, and encouraging internal mobility.
- Performance Evaluation: Measuring competencies and outcomes rather than tenure, focusing on concrete results like project success or innovation contributions to foster a merit-driven culture.
Globally, companies like Google and Microsoft have eliminated degree requirements for many roles, reflecting a broader shift toward skills-based approaches.
Benefits of a Skills-Based Approach
A skills-based strategy delivers measurable advantages:
- Diversified Talent Pool: By removing degree requirements, companies can hire from a 20% larger pool of candidates, including people with unique backgrounds who may not have formal education but have strong skills (LinkedIn Workforce Report, 2024). This opens doors for talent who might otherwise be overlooked.
- Enhanced Innovation: Teams trained in relevant skills adapt quickly to new tools and technologies, leading to 15% higher innovation rates (McKinsey, 2023). This helps businesses stay ahead in fast-changing industries like tech or finance.
- Cost Savings: Focused training programs cut onboarding costs by 10-15% compared to hiring based on degrees (SHRM, 2024). Companies save money by teaching only the skills needed for the job.
- Improved Retention: Clear career paths based on skills keep employees motivated, reducing turnover by 25% (Gartner, 2024). Workers stay longer when they see opportunities to grow and succeed.
- Inclusivity: Skills-based hiring gives non-degree holders, including underrepresented groups like women or minorities, a fair chance at jobs, boosting diversity and supporting DEI goals. This creates a workplace that reflects a wide range of perspectives and strengthens team dynamics.
These benefits help organizations stay competitive in fast-evolving sectors.
Also Read - Top HRMS Software Features for 2025 & Beyond
Real-World Examples
Skills-based strategies are transforming hiring and training across industries. Below are examples of global companies successfully implementing these approaches, showing how they prioritize practical abilities over degrees to build diverse, agile teams:
- Google (Global): Google’s Career Certificates program trains learners in high-demand skills like data analytics and IT support, requiring no prior degree. Offered through online platforms like Coursera, these short, focused courses prepare participants for real-world roles. In 2024, Google reported that 75% of certificate graduates secured jobs within six months, proving that skills-based training can quickly lead to employment in tech fields (Google, 2024). This approach helps Google tap into a broader talent pool, including non-traditional candidates, while addressing industry skill shortages.
- IBM (Global): IBM’s SkillsBuild platform provides free, accessible training in areas like AI, cybersecurity, and cloud computing, targeting non-degree holders. By offering micro-credentials and practical projects, SkillsBuild equips learners with job-ready skills, enabling them to fill technical roles in industries facing talent gaps. IBM’s focus on skills over credentials has allowed it to hire diverse candidates, including those without formal education, strengthening its global workforce (IBM, 2024).
- Siemens (Global): Siemens, a leader in manufacturing, uses skills-based assessments like technical simulations and problem-solving tests to hire for roles in automation and engineering. By focusing on candidates’ abilities rather than degrees, Siemens has increased workforce diversity by 20%, bringing in talent from varied backgrounds, including women and underrepresented groups (Siemens, 2024). This approach ensures employees have the practical skills needed for advanced manufacturing, enhancing team innovation and adaptability.
- Shopify (Global): The e-commerce platform Shopify employs coding challenges, such as those hosted on platforms like HackerRank, to evaluate developers during hiring. This method assesses real-world coding skills, reducing reliance on academic credentials and enabling Shopify to build agile, high-performing teams. By prioritizing practical ability, Shopify has streamlined its hiring process and attracted diverse talent, boosting team creativity and responsiveness in the fast-paced retail sector (Shopify, 2024).
These cases demonstrate how skills-based strategies succeed across tech, manufacturing, and retail by focusing on practical abilities, fostering diversity, and meeting industry demands efficiently.
Challenges and Solutions
- Challenge: Resistance to Change
HR teams and managers often favor degree-based hiring as it feels familiar and “safe,” fearing that skills-based models may lower standards.
Solution: Launch pilot programs in specific departments to test skills-based hiring. Share data like 20% wider talent pools and faster hiring to gain leadership support. Conduct workshops with case studies from Google or IBM.
- Challenge: Assessing Skills
Measuring hard skills (e.g., coding) is straightforward, but soft skills like collaboration or adaptability are harder to evaluate.
Solution: Use AI-powered tools like TestGorilla or HackerRank for technical roles and behavioral assessment platforms for soft skills, reducing bias and improving accuracy.
- Challenge: Training Costs
Upskilling programs require investment in content and time, challenging for SMEs.
Solution: Partner with platforms like Coursera, LinkedIn Learning, or edX for affordable micro-credentials and bootcamps. Corporate partnerships can secure bulk discounts (World Economic Forum, 2024).
- Challenge: Cultural Bias
Degrees are often seen as status symbols, influencing perceptions of competence.
Solution: Run awareness campaigns highlighting the success stories of non-degree holders. Engage leadership to endorse skills-first initiatives (OECD, 2025).
- Challenge: Skills Tracking
Mapping and updating skills across large organizations is resource-intensive.
Solution: Implement AI-driven platforms like Gloat, Degreed, or Fuel50 for real-time skills inventories and talent marketplaces, reducing administrative burden (Gartner, 2024).
Practical Strategies to Build a Skills-Based Approach
To shift to a skills-based talent management strategy, organizations can follow these actionable steps. Each strategy is designed to prioritize practical abilities over degrees, ensuring teams are equipped for 2025’s dynamic workplace:
-
Conduct a Skills Audit: Start by mapping out the skills your workforce already has and identifying gaps that need filling. Use employee surveys, performance reviews, or AI tools like Degreed to analyze current capabilities in high-demand areas such as AI, data analytics, or cybersecurity. For example, a tech company might discover a shortage of cloud computing expertise, guiding targeted training efforts. This process creates a clear roadmap for hiring and upskilling, ensuring resources are used efficiently (Gartner, 2024).
-
Revamp Hiring: Move away from degree-based hiring by using practical assessments like coding challenges, job simulations, or situational judgment tests. These tools, such as those offered by HackerRank or TestGorilla, evaluate candidates’ real-world problem-solving skills, making hiring fairer and more accurate. For instance, a finance firm might use a simulation to test analytical skills instead of requiring an MBA. This approach opens opportunities to diverse talent and reduces bias (SHRM, 2024).
-
Invest in Upskilling: Partner with affordable online platforms like Coursera, LinkedIn Learning, or edX to provide micro-credentials and bootcamps. These short, focused programs teach specific skills, like Python programming or digital marketing, without the time and cost of long degrees. For example, a retail company could train staff in e-commerce tools in just weeks, keeping employees current with industry trends. Corporate partnerships can also secure discounts, making training cost-effective (World Economic Forum, 2024).
-
Design Skills-Based Career Paths: Create clear, transparent career frameworks that reward skill mastery over years of service. For example, a junior coder could advance to an AI specialist role by earning certifications in machine learning and completing internal projects. This approach motivates employees by showing a clear path to growth, boosts engagement, and reduces the need for external hiring. Tools like Gloat can map these paths digitally, making them easy to follow (McKinsey, 2021)
-
Leverage Technology: Use AI-driven platforms like Eightfold AI, Gloat, or Fuel50 to recommend personalized learning paths and match employees to internal job opportunities. For instance, an employee skilled in data analysis could be suggested for a new analytics project based on their profile. These tools track skills in real time, reducing administrative work and helping retain talent by aligning roles with evolving abilities. This fosters agility and keeps teams future-ready.
-
Promote Continuous Learning: Encourage a culture of ongoing learning by offering incentives like digital badges, certifications, or small bonuses for completing training programs. Integrate learning goals into performance reviews to emphasize their importance. For example, a healthcare company might reward nurses for completing a digital health course, improving patient care. This approach keeps employees motivated and ensures skills stay relevant in fast-changing industries (Harvard Business Review, 2021).
-
Engage Leadership: Train managers to focus on skills and results when evaluating employees, rather than degrees or years of experience. For instance, a manager might assess a team member’s project outcomes or problem-solving skills instead of their academic background. Workshops showcasing success stories from skills-based firms like Google can build buy-in. When leaders champion this approach, it sets a skills-first culture across the organization (SHRM, 2024).
-
Measure Success: Track key performance indicators (KPIs) like productivity, employee retention, and workforce diversity to evaluate the impact of your skills-based strategy. For example, a company might measure how upskilling reduces project delays or increases diverse hires. Use tools like CultureAmp for real-time feedback to refine your approach. Sharing these results with stakeholders demonstrates clear return on investment (ROI), securing ongoing support (Gartner, 2024).
Key Trends for 2025
As the workplace evolves, several trends are shaping skills-based talent management in 2025. These trends help organizations stay competitive by addressing talent shortages, embracing technology, and promoting inclusivity. Here’s a detailed look at each:
-
AI-Driven Skills Mapping: Tools like Gloat and Eightfold AI, now used by 60% of global firms, track employee skills in real time to guide hiring and training decisions. For example, these platforms analyze an employee’s skills, like data analysis or project management, and suggest training or roles that match their strengths. This ensures companies hire the right talent and upskill employees efficiently, saving time and reducing costs in fast-paced industries like tech and finance.
-
Micro-Credentialing: Short, targeted courses, such as Google Career Certificates, allow workers to quickly learn in-demand skills like IT support or digital marketing without long degree programs. Adopted by 50% of tech firms, these programs help employees stay current in rapidly changing fields (Forbes, 2024). For instance, a retail worker could earn a certificate in e-commerce in weeks, boosting their ability to contribute immediately. This trend makes training flexible and accessible for all.
-
Gig Economy Integration: Platforms like Upwork and Fiverr offer skills-based training for freelancers, with 70% of companies hiring them for specialized tasks like graphic design or software development (Upwork, 2024). This allows businesses to tap into a global pool of skilled workers for short-term projects, while freelancers gain certifications to boost their careers. For example, a company might hire a freelance AI expert for a specific project, saving costs on full-time hires.
-
Soft Skills Focus: With 65% of organizations using behavioral assessments to evaluate skills like adaptability, collaboration, and emotional intelligence, these “soft” skills are now critical for leadership roles (SHRM, 2024). Unlike technical skills, soft skills help teams navigate hybrid work and complex projects. For instance, a manager with strong collaboration skills can unite a remote team, improving outcomes. Tools like TestGorilla assess these traits to ensure fair hiring and development.
-
DEI Alignment: Skills-based hiring removes degree barriers, leading to 30% more women and underrepresented groups in tech roles. By focusing on skills, companies create fairer opportunities for diverse talent, such as self-taught coders or career switchers. This trend builds inclusive workplaces where varied perspectives drive innovation, benefiting industries like healthcare and retail that rely on diverse teams.
-
Automation Upskilling: With 40% of jobs at risk of automation, companies are investing heavily in AI and data literacy training to prepare workers for future roles (World Economic Forum, 2024). For example, a manufacturing firm might train workers to operate AI-driven machines, ensuring they stay relevant. This trend helps employees adapt to automation while helping businesses maintain productivity in an increasingly tech-driven world.
These trends show how skills-based approaches are transforming workplaces, making them more agile, inclusive, and ready for 2025’s challenges.
Also Read - 12 Must-Have HRMS Software Features for 2025
Skills vs. Degrees: A Comparison
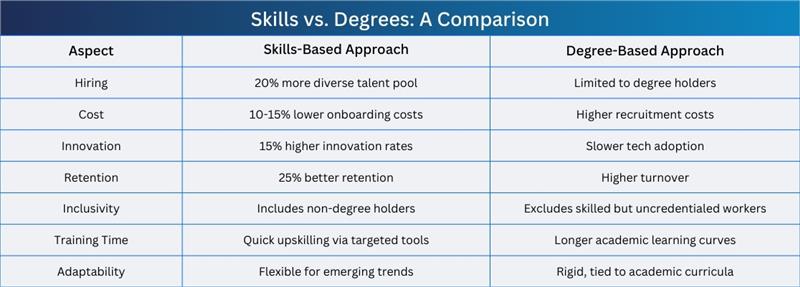
Conclusion
A skills-based talent management strategy is critical in 2025 to navigate talent shortages, drive innovation, and promote inclusivity. By starting with a skills audit, leveraging AI tools, and partnering with training platforms like Coursera, organizations can build future-ready teams. Resources like SHRM’s reports or LinkedIn Learning can guide implementation. Prioritizing skills ensures a competitive, adaptable workforce in a dynamic global economy.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is a skills-based talent management strategy?
It focuses on hiring, training, and promoting based on abilities, using assessments and targeted development.
- Why is it critical in 2025?
It addresses talent shortages, boosts innovation, and aligns with automation and diversity trends.
- How can SMEs adopt this approach?
Use low-cost audits and platforms like Coursera for affordable training.
- What are the main challenges?
Resistance, assessment accuracy, and costs, overcome with pilot programs, AI tools, and partnerships.
- Is it applicable to all industries?
Yes, from tech (coding) to healthcare (technical training), tailored to specific needs.
 ×
×
 ZYNO Manufacturing ERP
+
ZYNO Manufacturing ERP
+
 Production Planning & Scheduling
Production Planning & Scheduling
 Expense Management Software
Expense Management Software
 Mobile App
Mobile App
 AI-Powered Demand Forecasting
AI-Powered Demand Forecasting
 Field Service Management
Field Service Management
 Ticket Management Software
Ticket Management Software
 Training Management System
Training Management System
 Document Management
Document Management
 Human Resources & Time Tracking
Human Resources & Time Tracking
 Analytics & Reporting
Analytics & Reporting
 Quotes & Sales Orders (Manufacturing CRM)
Quotes & Sales Orders (Manufacturing CRM)
 Finance & Cost Accounting
Finance & Cost Accounting
 Shop-Floor & MES Reporting
Shop-Floor & MES Reporting
 Statutory Compliance & Taxation
Statutory Compliance & Taxation
 Subcontracting & Outside Processing
Subcontracting & Outside Processing
 Project-Based Manufacturing
Project-Based Manufacturing
 Quality Control & Compliance
Quality Control & Compliance
 Maintenance & Asset Management
Maintenance & Asset Management
 Procurement & Supplier Management
Procurement & Supplier Management
 Inventory & Warehouse Management
Inventory & Warehouse Management
 Vendor Management Software
Vendor Management Software
.webp) Bill of Materials (BOM)
Bill of Materials (BOM)
 Product Configurator
Product Configurator
 ZYNO Procurement
+
ZYNO Procurement
+
 ZYNO CRM
+
ZYNO CRM
+
 ZYNO HRMS
+
ZYNO HRMS
+
 Integrated recruitment
Integrated recruitment
 Learning management
Learning management
 Mobile app
Mobile app
 HR chatbot
HR chatbot
 Custom services
Custom services
 HR automation
HR automation
 Business chat and collaboration
Business chat and collaboration
 Employee engagement
Employee engagement
 Integrated travel and expense
Integrated travel and expense
 Integrated payroll software
Integrated payroll software
 Compensation management
Compensation management
 Onboarding
Onboarding
 Performance management
Performance management
 HR analytics
HR analytics
 Digital Document management
Digital Document management
 HR help desk
HR help desk
 Timesheets
Timesheets
 Leave management
Leave management
 Shift management
Shift management
 Attendance management
Attendance management
 Employee management
Employee management
 Integrations
Integrations
 ZYNO Assets
+
ZYNO Assets
+
.webp) ZYNO EduVibe
+
ZYNO EduVibe
+
 ZYNO Upskill
+
ZYNO Upskill
+
 ZYNO Rewards
+
ZYNO Rewards
+
 ZYNO HIMS
+
ZYNO HIMS
+
 ZYNO Expenz
+
ZYNO Expenz
+
 ZYNO Legal
+
ZYNO Legal
+
 ZYNO Audit
+
ZYNO Audit
+
 ZYNO Retail
+
ZYNO Retail
+
 ZYNO Recruit
+
ZYNO Recruit
+
 ZYNO Projects
+
ZYNO Projects
+
 ZYNO Books
+
ZYNO Books
+
 ZYNO POS
+
ZYNO POS
+
 Search Engine Optimization
+
Search Engine Optimization
+
 Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)
 Paid Media & Advertising
+
Paid Media & Advertising
+
 Amazon Marketing Services
+
Amazon Marketing Services
+
 Social Media Marketing
+
Social Media Marketing
+
 Content Marketing
+
Content Marketing
+
 Conversion Rate Optimization
+
Conversion Rate Optimization
+
 Online Reputation Management (ORM)
+
Online Reputation Management (ORM)
+
 Analytics, Strategy & Consulting
+
Analytics, Strategy & Consulting
+
 Brand Management
Brand Management
 E Commerce Marketing
E Commerce Marketing




.webp)



-1.webp)


.webp)




































.webp)






























































.webp)






.webp)






.webp)
.webp)














































































.webp)
.jpg)

.jpg)
.png)











.jpg)










.jpg)









.webp)



