In 2026, businesses are racing to stay agile, resilient, and cost-efficient. From global trade disruptions and geopolitical tensions to digital transformation and sustainability pressures, organisations are constantly rethinking how they acquire and deliver value.
Amid this backdrop, understanding procurement and supply chain functions is no longer an academic exercise — it’s a strategic imperative. While these terms are often used interchangeably, they are not the same. In fact, misunderstanding the difference between procurement and supply chain management can lead to fragmented operations, poor decision-making, and missed growth opportunities. For business leaders, professionals, and decision-makers, understanding how these two functions work together — and where they differ — is essential for building resilient and future-ready organisations.
In this blog, we’ll journey through both concepts in depth — from definitions and roles to processes, real-world applications, and strategic trends shaping the future.
What is Procurement ?
Procurement refers to the structured and strategic process through which an organisation acquires goods and services essential for its operations. Beyond purchasing, it focuses on value creation by balancing cost efficiency, quality standards, timely delivery, supplier reliability, regulatory compliance, and long-term business sustainability through well-managed sourcing decisions.
Here’s what procurement typically involves:
-
Identifying business needs and specifications
This step involves understanding internal requirements, defining quantities, quality standards, timelines, and technical specifications to ensure procurement aligns with operational and strategic business goals.
-
Researching and selecting the right suppliers
Procurement teams evaluate potential suppliers based on capability, reliability, pricing, compliance, and risk factors to ensure consistent supply and long-term partnership value.
-
Negotiating contracts and pricing
Negotiation focuses on securing favourable pricing, delivery terms, service levels, and risk-sharing clauses while protecting the organisation’s legal, financial, and operational interests.
-
Monitoring supplier performance and compliance
This ensures suppliers consistently meet agreed quality, delivery, ethical, and regulatory standards, helping organisations reduce risk and maintain operational continuity.
-
Managing purchase orders, invoices, and payments
Procurement oversees transactional accuracy by ensuring purchase orders, invoices, and payments align with contracts, improving financial control and audit readiness.
-
Building long-term strategic supplier relationships
Strong supplier relationships foster collaboration, innovation, risk mitigation, and cost optimisation, enabling organisations to gain competitive advantage over time.
Role of Procurement in an Organization
Cost Optimization and Value Creation
Procurement plays a crucial role in controlling organisational spending by negotiating favourable pricing, identifying cost-saving opportunities, and ensuring optimal value rather than simply choosing the lowest price.
Supplier Selection and Relationship Management
Procurement is responsible for identifying reliable suppliers and building long-term partnerships that ensure consistency, innovation, and mutual growth while reducing dependency-related risks.
Risk Management and Business Continuity
By evaluating supplier risks, diversifying sourcing strategies, and ensuring contractual safeguards, procurement helps protect the organisation from supply disruptions and operational uncertainties.
Compliance and Governance
Procurement ensures all purchasing activities comply with internal policies, legal regulations, and industry standards, reducing exposure to financial, legal, and reputational risks.
Supporting Strategic Business Goals
Modern procurement aligns sourcing decisions with organisational objectives such as sustainability, digital transformation, and expansion, making it a strategic contributor to overall business success.
Importance of Procurement in Modern Businesses
Drives Cost Efficiency and Financial Control
Procurement helps organisations control spending through planned sourcing, effective negotiations, and contract management, ensuring cost efficiency without sacrificing quality or operational reliability.
Ensures Business Continuity and Supply Stability
By identifying reliable suppliers and diversifying sourcing strategies, procurement reduces supply risks and ensures uninterrupted operations during market volatility or disruptions.
Strengthens Supplier Relationships and Collaboration
Procurement builds long-term supplier partnerships that encourage collaboration, improve service quality, support innovation, and create mutual value across the supply chain.
Mitigates Risk and Enhances Compliance
Through supplier evaluation and compliance monitoring, procurement minimises legal, financial, and operational risks while maintaining regulatory and governance standards.
Supports Strategic Business and Growth Objectives
Procurement aligns sourcing decisions with business goals, enabling scalability, flexibility, and competitive advantage in dynamic market environments.
Enables Sustainable and Responsible Business Practices
Procurement promotes ethical sourcing and sustainability by ensuring suppliers meet environmental, social, and governance standards, strengthening brand trust and accountability.

What Is Supply Chain Management?
Supply chain management (SCM) refers to the integrated approach used to plan, manage, and optimise the flow of goods, services, information, and finances across an organisation’s entire value network. It connects suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and customers to ensure efficiency, responsiveness, and consistent value delivery.
Supply chain management includes:
-
Procurement (sourcing of goods and services)
Ensures timely availability of quality materials and services by selecting reliable suppliers and managing sourcing strategies aligned with business demand.
-
Manufacturing and production planning
Coordinates resources, schedules, and capacity to meet demand efficiently while minimising waste, delays, and production costs.
-
Inventory and warehouse management
Manages stock levels and storage operations to balance supply availability, carrying costs, and order fulfilment requirements.
-
Logistics and transportation
Oversees the movement of goods between locations, ensuring timely, cost-effective, and secure delivery across supply chain networks.
-
Demand forecasting and planning
Uses historical data and market insights to predict customer demand and guide production, procurement, and distribution decisions.
-
Distribution and delivery coordination
Ensures finished products reach customers efficiently through optimised distribution channels and last-mile delivery strategies.
-
Returns and after-sales service
Manages product returns, replacements, and support services to maintain customer satisfaction and recover value where possible.
Benefits of Supply Chain Management
Improved Operational Efficiency
Effective supply chain management streamlines processes, reduces delays, and eliminates redundancies, enabling organisations to operate faster, smoother, and with better resource utilisation.
Cost Reduction and Better Profitability
By optimising sourcing, inventory, and logistics, supply chain management helps lower operational costs while improving margins without compromising service quality.
Enhanced Customer Satisfaction
Well-managed supply chains ensure timely deliveries, product availability, and consistent service levels, directly improving customer trust and long-term loyalty.
Greater Visibility and Control
Supply chain management provides end-to-end visibility across suppliers, inventory, and logistics, enabling better decision-making and quicker response to disruptions.
Increased Resilience and Risk Management
A strong supply chain reduces dependency on single sources, mitigates disruptions, and ensures business continuity in uncertain market conditions.
Core Components of Supply Chain Management
Procurement and Supplier Management
Focuses on sourcing reliable suppliers, negotiating contracts, and maintaining supplier relationships to ensure quality, cost efficiency, and supply reliability.
Demand Planning and Forecasting
Uses data and market insights to anticipate customer demand, aligning production, procurement, and distribution activities accordingly.
Manufacturing and Production Management
Oversees production planning, capacity utilisation, and process efficiency to meet demand while controlling costs and maintaining quality standards.
Inventory and Warehouse Management
Manages stock levels, storage, and material handling to ensure product availability while minimising holding costs and wastage.
Logistics and Transportation Management
Coordinates the movement of goods across the supply chain, ensuring timely, secure, and cost-effective delivery.
Distribution and Customer Fulfilment
Ensures finished products reach customers through efficient distribution networks and last-mile delivery, supporting service excellence and customer satisfaction.
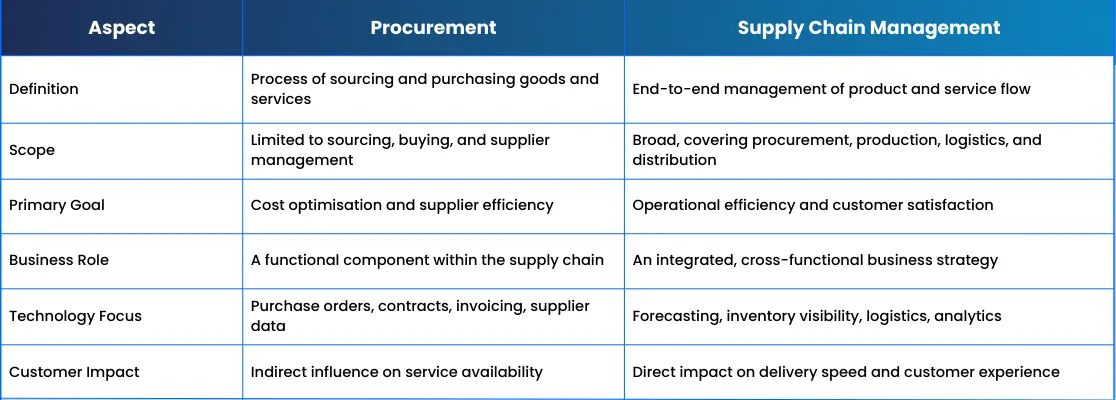
Procurement vs. Supply Chain: Key Differences
Although closely related, procurement focuses on purchasing goods and services, while supply chain management manages their entire flow. Understanding this difference helps businesses improve processes, roles, and technology decisions.
Below are the six key differences that clearly separate procurement from supply chain management.
Scope of Operations
Procurement operates within a limited scope, concentrating mainly on sourcing, purchasing, and supplier management.
Supply chain management has a broader scope, covering procurement, production, inventory, logistics, distribution, and customer fulfilment.
Primary Objective
The main goal of procurement is to obtain goods and services at the best possible cost, quality, and terms.
Supply chain management focuses on optimising the end-to-end flow of materials, information, and products to meet customer demand efficiently.
Position in the Business Process
Procurement is one function within the supply chain and acts as its starting point.
Supply chain management integrates procurement with manufacturing, warehousing, transportation, and delivery activities.
Strategic vs. Operational Focus
Procurement balances operational purchasing tasks with strategic supplier negotiations and cost control.
Supply chain management is more strategic, aligning multiple functions to improve resilience, speed, and overall business performance.
Technology and Data Usage
Procurement Software primarily manage supplier data, purchase orders, contracts, and invoices.
Supply chain systems leverage advanced analytics, forecasting, and automation to manage demand planning, logistics, and inventory visibility.
Impact on Customer Experience
Procurement indirectly affects customers by ensuring materials and services are available on time.
Supply chain management directly impacts customer satisfaction through delivery speed, order accuracy, and service reliability.
Procurement vs. Supply Chain Management: Comparison Table
Procurement in Supply Chain Management
Procurement is a critical function within the broader supply chain, and understanding procurement in supply chain management is essential for building efficient, resilient, and customer-centric operations. It ensures that the right materials and services are sourced at the right cost, quality, and time, forming the foundation for smooth production and delivery processes.
In practice, procurement in supply chain management involves several interconnected activities:
-
Need Identification: Internal teams determine what goods or services are required, setting clear specifications, timelines, and budgets that align with business objectives.
-
Supplier Sourcing and Evaluation: Procurement teams assess potential suppliers based on reliability, cost-effectiveness, compliance, and long-term strategic value. This step ensures the supply chain has dependable partners.
-
Negotiation and Contract Management: Terms, pricing, service levels, and delivery schedules are negotiated carefully to balance cost savings with operational efficiency, while legally binding contracts protect both parties.
-
Execution and Integration: Approved purchase orders are processed, and procured items are seamlessly integrated into production planning, inventory management, logistics, and distribution workflows. This guarantees continuity and responsiveness across the supply chain.
-
Monitoring and Continuous Improvement: Supplier performance, delivery timelines, and quality standards are continually tracked. Data-driven insights help refine sourcing strategies and enhance the overall efficiency of the supply chain.
By focusing on procurement in supply chain management, organisations can not only reduce costs and improve supplier relationships but also strengthen overall supply chain performance, mitigate risks, and ensure that customer demands are met reliably.
Why This Difference Matters for Businesses
Understanding the distinction isn’t just academic; it directly impacts business performance.
Risk Management
With rising cyber threats, geopolitical uncertainty, and supply shortages, aligned procurement and supply chain strategies help organisations identify risks early, strengthen supplier controls, and protect operational continuity.
Cost Control & Competitiveness
Procurement secures quality inputs at optimal costs, while supply chain teams balance these savings with logistics, inventory, and service efficiency to maintain competitiveness without compromising customer expectations.
Strategic Alignment
Organisations integrating procurement and supply chain processes respond faster to disruptions, improve agility, and align sourcing, planning, and execution with long-term business and market objectives.
Operational Visibility & Decision-Making
End-to-end visibility across procurement and supply chain activities enables data-driven decisions, improves forecasting accuracy, and allows businesses to proactively address bottlenecks and performance gaps.
Customer Experience & Service Reliability
Strong coordination between procurement and supply chain functions ensures product availability, timely delivery, and consistent service levels, directly enhancing customer satisfaction and brand trust.

Trends Shaping Procurement and Supply Chain in 2025
Modern businesses are also transforming these functions through digital innovation:
AI & Automation
From predictive analytics to smart procurement tools, organisations use AI to improve demand forecasting, supplier risk management, and process automation efficiently.
Sustainability and ESG
Environmental, Social, and Governance criteria are integrated into supplier selection and supply chain strategy to meet ethical and sustainable business requirements.
Resilience Over Cost
Businesses prioritize resilience over cost, building redundancy and flexibility into supply chains and procurement strategies to reduce vulnerability to disruptions.
Blockchain for Transparency
Blockchain ensures secure, transparent, and traceable transactions across the supply chain, improving trust, reducing fraud, and enhancing supplier accountability.
Digital Collaboration Platforms
Cloud-based collaboration tools enable real-time communication between stakeholders, improving coordination, workflow efficiency, and faster decision-making across procurement and supply chain networks.
Common Misconceptions About Procurement and Supply Chain
Let’s clarify some usual misunderstandings:
-
Procurement and purchasing are the same.
Purchasing is transactional (placing orders); procurement is broader and strategic.
-
Supply chain is only logistics.
SCM is far more than logistics — it includes planning, procurement, production, demand forecasting, and customer delivery.
-
Procurement only saves money.
In reality, it drives innovation, strengthens supplier partnerships, and enhances risk preparedness.
-
Procurement has no impact on customer satisfaction.
In reality, efficient procurement ensures timely delivery of quality materials, which directly affects product quality, service levels, and customer satisfaction.
-
Supply chain management is only relevant for large businesses.
Even small and medium enterprises benefit from SCM through cost optimization, efficient operations, and better supplier and customer relationships.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between procurement and supply chain management is crucial for modern business success. While procurement homes in on sourcing and supplier value, supply chain management orchestrates the entire journey from raw materials to customer delivery.
Together, they create a resilient, cost-efficient, and customer-centric business engine — and professionals who master both areas are among the most sought-after in today’s competitive landscape. Take the next step in your career — explore Elite Mindz’s industry-aligned courses in procurement and supply chain management, tailored for real-world impact.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main difference between procurement and supply chain management?
Procurement focuses on sourcing and acquiring goods/services, whereas supply chain management oversees the end-to-end flow of products from raw materials to customer delivery.
Is procurement part of supply chain management?
Yes — procurement is a key function within the broader supply chain framework that ensures inputs are sourced effectively.
How does procurement impact supply chain performance?
Procurement influences cost, supplier reliability, and availability of materials — all of which affect production planning and delivery performance.
What skills are important for procurement professionals?
Key skills include negotiation, supplier management, data analysis, risk assessment, and contract governance.
What trends are shaping procurement and supply chain management in 2025?
Digital transformation (AI/analytics), sustainability and ESG integration, resilience planning, and strategic sourcing are top trends.
 ×
×
 ZYNO Manufacturing ERP
+
ZYNO Manufacturing ERP
+
 Production Planning & Scheduling
Production Planning & Scheduling
 Quotes & Sales Orders (Manufacturing CRM)
Quotes & Sales Orders (Manufacturing CRM)
 Product Configurator
Product Configurator
 Mobile App
Mobile App
 AI-Powered Demand Forecasting
AI-Powered Demand Forecasting
 Field Service Management
Field Service Management
 Ticket Management Software
Ticket Management Software
 Training Management System
Training Management System
 Document Management
Document Management
 Human Resources & Time Tracking
Human Resources & Time Tracking
 Analytics & Reporting
Analytics & Reporting
 Expense Management Software
Expense Management Software
.webp) Bill of Materials (BOM)
Bill of Materials (BOM)
 Finance & Cost Accounting
Finance & Cost Accounting
 Statutory Compliance & Taxation
Statutory Compliance & Taxation
 Subcontracting & Outside Processing
Subcontracting & Outside Processing
 Project-Based Manufacturing
Project-Based Manufacturing
 Quality Control & Compliance
Quality Control & Compliance
 Maintenance & Asset Management
Maintenance & Asset Management
 Procurement & Supplier Management
Procurement & Supplier Management
 Inventory & Warehouse Management
Inventory & Warehouse Management
 Vendor Management Software
Vendor Management Software
 Live Shop-Floor
Live Shop-Floor
 ZYNO Procurement
+
ZYNO Procurement
+
 ZYNO CRM
+
ZYNO CRM
+
 ZYNO HRMS
+
ZYNO HRMS
+
 Integrated recruitment
Integrated recruitment
 Learning management
Learning management
 Mobile app
Mobile app
 HR chatbot
HR chatbot
 Custom services
Custom services
 HR automation
HR automation
 Business chat and collaboration
Business chat and collaboration
 Employee engagement
Employee engagement
 Integrated travel and expense
Integrated travel and expense
 Integrated payroll software
Integrated payroll software
 Compensation management
Compensation management
 Onboarding
Onboarding
 Performance management
Performance management
 HR analytics
HR analytics
 Digital Document management
Digital Document management
 HR help desk
HR help desk
 Timesheets
Timesheets
 Leave management
Leave management
 Shift management
Shift management
 Attendance management
Attendance management
 Employee management
Employee management
 Integrations
Integrations
 ZYNO Assets
+
ZYNO Assets
+
.webp) ZYNO EduVibe
+
ZYNO EduVibe
+
 ZYNO Upskill
+
ZYNO Upskill
+
 ZYNO Rewards
+
ZYNO Rewards
+
 ZYNO HIMS
+
ZYNO HIMS
+
 ZYNO Expenz
+
ZYNO Expenz
+
 ZYNO Legal
+
ZYNO Legal
+
 ZYNO Audit
+
ZYNO Audit
+
 ZYNO Retail
+
ZYNO Retail
+
 ZYNO Recruit
+
ZYNO Recruit
+
 ZYNO Projects
+
ZYNO Projects
+
 ZYNO Books
+
ZYNO Books
+
 ZYNO POS
+
ZYNO POS
+
 Search Engine Optimization
+
Search Engine Optimization
+
 Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)
 Paid Media & Advertising
+
Paid Media & Advertising
+
 Amazon Marketing Services
+
Amazon Marketing Services
+
 Social Media Marketing
+
Social Media Marketing
+
 Content Marketing
+
Content Marketing
+
 Conversion Rate Optimization
+
Conversion Rate Optimization
+
 Online Reputation Management (ORM)
+
Online Reputation Management (ORM)
+
 Analytics, Strategy & Consulting
+
Analytics, Strategy & Consulting
+
 Brand Management
Brand Management
 E Commerce Marketing
E Commerce Marketing




.webp)



-1.webp)


.webp)




































.webp)






























































.webp)






.webp)






.webp)
.webp)





















































































.jpg)








.png)
_converted.webp)



.webp)



